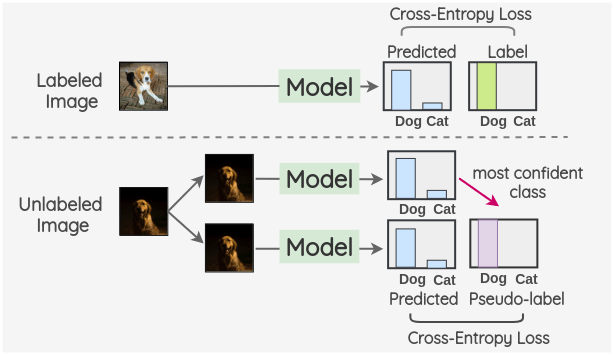
Semi-Supervised Learning with few labels
Published:
Project Title: Enhancing Performance of Self-Supervised Models with Limited Labeled Data
Project Overview:
This project focuses on improving the performance of self-supervised learning models, especially in scenarios where only a small amount of labeled data is available. The core objective is to enhance the quality of the output representations from these models, thereby boosting their performance in various downstream tasks.
Key Objectives:
Enhance Output Representations:
- The primary goal is to improve the robustness and discriminative power of the features learned by self-supervised models, ensuring high-quality representations even with limited labeled data.
Combine Self-Supervision with Supervised Learning:
- By integrating a small amount of labeled data into the training process, the project aims to synergize the strengths of both self-supervised and supervised learning paradigms, thereby enhancing overall model performance.
Methodology:
The project employs a strategic two-step approach to achieve these objectives:
Incorporate a Linear Supervision Layer:
- Initial Stage: During the initial training phase, a linear layer is added on top of the self-supervised model. This layer leverages the available labeled data to provide supervised signals that guide the learning process. This step ensures that the learned representations are well-grounded in the labeled data, improving their quality and relevance to the target tasks.
Enforce High Correlation Among Same-Class Inputs:
- Correlation Enforcement: To further refine the output representations, the model is trained to maximize the correlation between representations of inputs belonging to the same class. This objective encourages the model to produce similar representations for same-class inputs, thereby reinforcing its ability to distinguish between different classes effectively.
Tools and Technologies:
- Python: The primary programming language used for the implementation of the project.
- PyTorch: The main deep learning framework utilized for building and training the models, known for its flexibility and robust support for dynamic computation graphs.
- PyTorch Lightning: A higher-level interface for PyTorch that simplifies the training process and provides utilities for efficient experimentation, facilitating the implementation of complex training loops and model checkpoints.
- Weights & Biases (WandB): A tool for experiment tracking and visualization, helping to monitor model performance, log experiments, and visualize the progression of training.
- Google Colab: An online platform offering free GPU resources, which is used for running experiments and providing a collaborative environment for development and testing.
Domain Knowledge:
- Computer Vision: Understanding the principles and techniques used in image processing and analysis, which is crucial for designing effective self-supervised and semi-supervised learning models.
- Self-Supervised Learning: Techniques where the model learns to represent data without labeled examples, typically by predicting parts of the input data from other parts.
- Semi-Supervised Learning: Approaches that utilize a small amount of labeled data alongside a larger amount of unlabeled data to enhance learning efficiency and performance.
Project Report:
The project’s results, methodologies, and findings are comprehensively documented in a report hosted on Weights & Biases. This report includes detailed explanations of the techniques used, experiments conducted, and the outcomes observed. The full report can be accessed here.
Outcome and Future Work:
Enhanced Model Performance:
- The project aims to push the boundaries of self-supervised learning by improving model performance in scenarios with limited labeled data, making the models more practical and effective for real-world applications.
Potential Enhancements:
- Future improvements may include exploring other model architectures, incorporating more sophisticated self-supervised learning techniques, and experimenting with larger and more diverse datasets to further enhance the robustness and generalizability of the models.
- Ongoing research and collaboration with other experts in the field can provide additional insights and opportunities for innovation in self-supervised and semi-supervised learning domains.