Specializing Large Language Models for Telecom Applications
Published:
Project Description: Enhancing Telecom Knowledge Tasks with Specialized LLMs
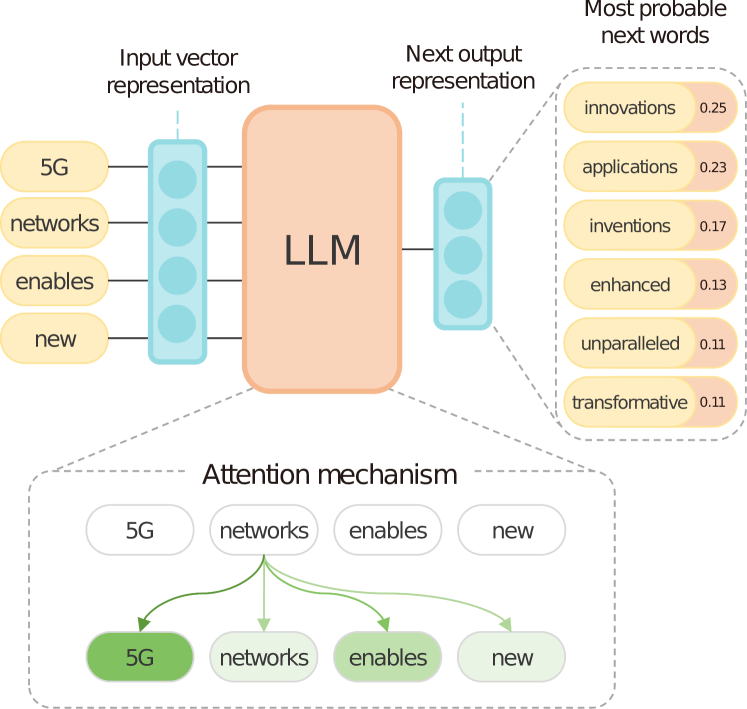
Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable capabilities in general text understanding and generation. However, their effectiveness can be limited when applied to highly specialized domains like telecommunications without specific adaptation. This project explores the specialization of LLMs to improve their performance on tasks requiring deep telecom industry knowledge.

Objective
The primary goal is to adapt and optimize a pre-trained Large Language Model, specifically Phi-3-mini-4k-instruct, for telecom-specific question-answering tasks. This involves fine-tuning the model on a specialized dataset to enhance its accuracy and relevance within the telecom domain.
Key Features
- Domain Specialization: Focuses on adapting a general-purpose LLM (Phi-3-mini-4k-instruct) to the specific nuances and terminology of the telecommunications sector.
- Fine-Tuning: Employs supervised fine-tuning techniques using a targeted dataset to improve the model’s ability to handle telecom-related queries.
- Specialized Dataset: Utilizes the TeleQnA competition dataset, which consists of multiple-choice questions specifically related to telecommunications, ensuring domain relevance.
- Performance Optimization: Aims to achieve measurable improvements in the model’s performance (e.g., accuracy) on telecom knowledge tasks compared to the base model.
Project Objectives:
- Fine-tune Phi-3-mini-4k-instruct on Telecom Knowledge:
- Train and optimize the Phi-3-mini-4k-instruct model to accurately respond to telecom-specific questions.
- Leverage advanced training techniques such as LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) for efficient model tuning, along with 4-bit quantization to handle large-scale data while reducing memory footprint.
- Overcome Common Challenges:
- Address the complexities of telecom-specific terminology and concepts.
- Reduce hallucinations common in LLMs when faced with domain-specific queries.
- Ensure responses are accurate and can be justified using telecom knowledge.
Methodology
The fine-tuning process included several key steps, leveraging efficient training techniques and domain-specific adjustments to ensure optimal model performance:
- Data Understanding and Preparation:
- The project utilized the TeleQnA dataset, ensuring the text data was properly structured and relevant for telecom knowledge tasks.
- Data preprocessing was performed using custom utilities to clean and prepare telecom text for model consumption.
- Model Selection and Fine-Tuning:
- Model Choice: Selected a suitable base LLM (Phi-3-mini-4k-instruct) known for its strong instruction-following capabilities, manageable size, and support for RoPE Scaling for extended context length.
- Model Fine-Tuning:
- Implemented parameter-efficient tuning using QLoRA, targeting specific layers for low-rank adaptation such as
q_proj,k_proj, andv_projmodules, which are critical for understanding attention in telecom-specific contexts.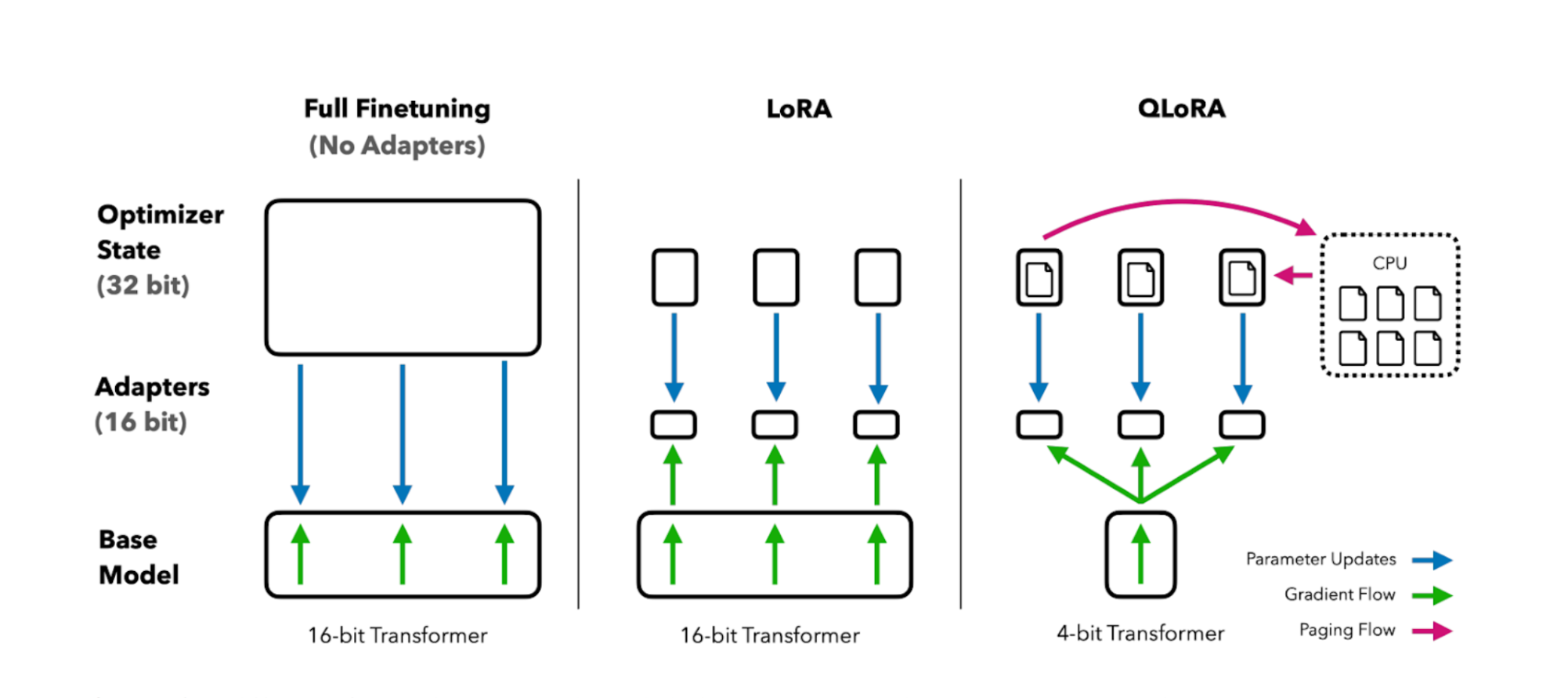
- Utilized gradient checkpointing and memory-efficient techniques like 4-bit quantization to minimize GPU memory consumption, making the process viable for longer sequences.
- Implemented parameter-efficient tuning using QLoRA, targeting specific layers for low-rank adaptation such as
- Training Setup:
- Training Configuration:
- Used SFTTrainer from the
trllibrary to manage the fine-tuning process. This allowed for flexible configurations with customized sequence length, packing strategy, and multi-GPU support for telecom-specific fine-tuning. - Batch sizes and learning rates were optimized based on the constraints of the telecom dataset, using AdamW optimizer with 8-bit precision to balance performance and memory efficiency.
- Used SFTTrainer from the
- Training Configuration:
- Mitigating Hallucinations and Fabrications:
- Focused on limiting fabricated responses by employing fact-checking mechanisms and reinforcement-based techniques to penalize hallucinations during the training process.
- Integrated post-processing steps, validating output against a trusted telecom knowledge base to ensure factual consistency.
- Evaluation:
- Evaluate the fine-tuned model’s performance on a held-out test set from the TeleQnA data or similar telecom-specific benchmarks.
- Analyze the results to understand the impact of fine-tuning on the model’s domain-specific knowledge and reasoning abilities.
Tools and Technologies
- Core Concepts: Large Language Models (LLMs), Fine-Tuning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Domain Adaptation, Question Answering
- Models: Phi-3-mini-4k-instruct
- Frameworks/Libraries:
- Python for coding and model management
- PyTorch / TensorFlow for model training and handling LLMs
- Hugging Face Transformers for accessing pre-trained language models
- Unsloth Libraries for fine-tuning and efficient memory utilization
- PEFT (Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning) libraries for LoRA implementation
- Accelerate for distributed training support
Technical Implementation:
The fine-tuning was implemented using the following key configurations:
- Sequence Length: Set to 2048 tokens to handle the longer context often found in telecom data.
- LoRA Parameters:
r=16,lora_alpha=16, with dropout and bias optimizations, ensuring efficient parameter updates during training.
- Training Optimizations:
- CUDA and GPU Settings: Optimized for GPU usage on Tesla-class hardware, ensuring fast execution and reduced memory overhead.
- Batch Size Adaptation: Dynamic batch size adjustments based on GPU memory, along with gradient accumulation to ensure stable training.
Applications
- Telecom Customer Support: Powering chatbots or virtual assistants with accurate telecom knowledge.
- Network Operations: Assisting technicians with troubleshooting guides and documentation retrieval.
- Sales and Marketing: Generating targeted content or answering product-specific questions.
- Internal Knowledge Management: Creating systems for employees to quickly find information within vast telecom documentation.
Outcome:
- Enhanced Accuracy: The model demonstrated improved performance in answering telecom-specific questions, outperforming earlier baselines like Falcon 7.5B.
- Improved Resource Utilization: By employing 4-bit quantization and LoRA, the model trained effectively on large datasets without exhausting GPU resources.
Future Work:
- Dataset Expansion: Continue expanding the dataset with more specialized telecom questions and edge cases.
- Model Scaling: Explore scaling the fine-tuning to larger models such as LLaMA-2 or incorporating RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) for even more accurate responses.
This project highlights the importance of domain specialization for LLMs and demonstrates a practical approach to enhancing their utility for specific industry applications like telecommunications.
Code: The full implementation is available here.